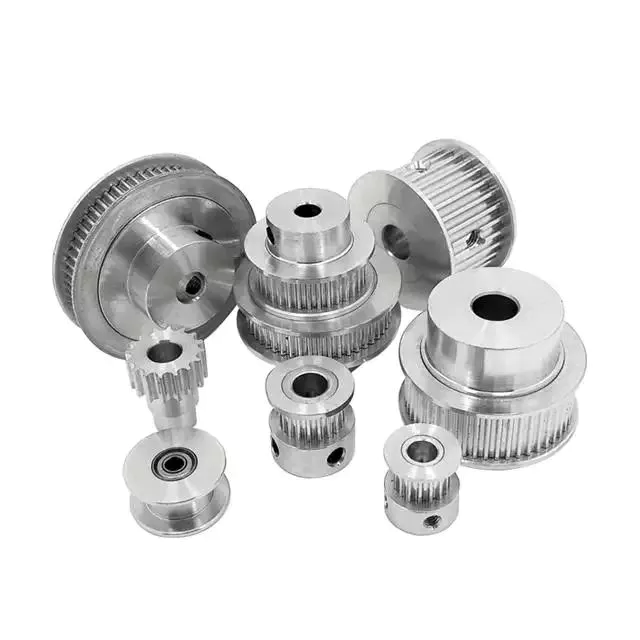
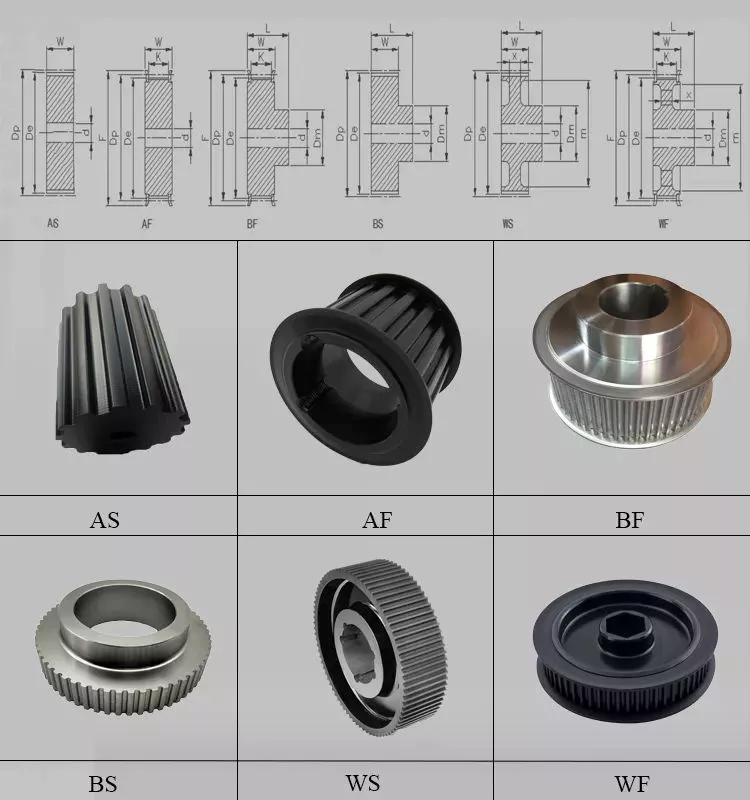
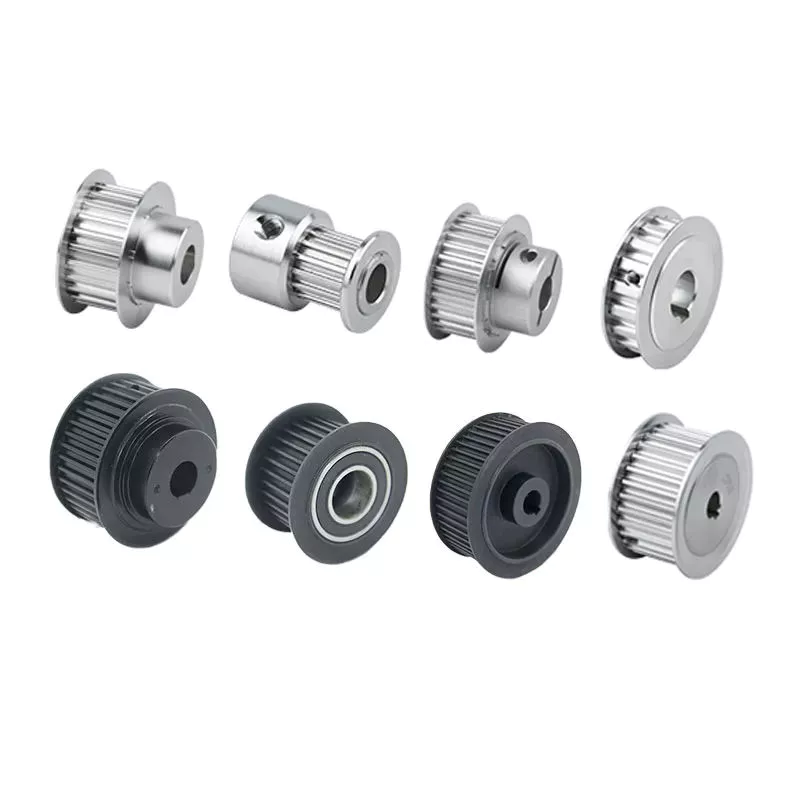
Product Description
V-belt pulley introduce:
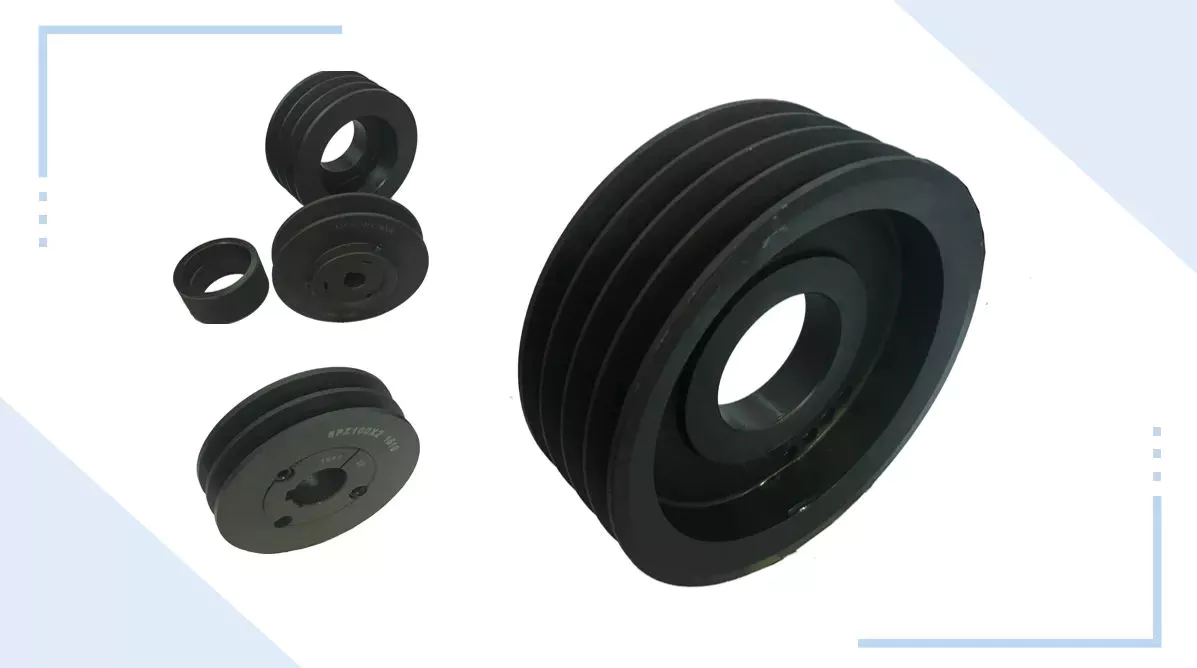
V- belt pulley of different types ( according to type and width of belts). The material used is cast iron EN-GJL-250 CHINAMFG EN 1561, and for only a few types it is steel C45 E CHINAMFG EN 10083-1. They have a small prebore that can be machined according to customers’ requirements. Moreover the most common types are available also with taperlock bore.
V belt pulley specifications
· European standards :
a) V-belt pulley for taper bushing: SPZ, SPA, SPB, SPC
b) Adjustable speed V-belt pulleys and variable speed pulleys
c) Flat belt pulleys and conveyor belt pulleys
· American standard:
a) Sheaves for taper bushing: 3V, 5V, 8V
b) Sheaves for QD bushings: 3V, 5V, 8V
c) Sheaves for split taper bushing: 3V, 5V, 8V
d) Sheaves for 3L, 4L or A, and 5L or B belts: AK, AKH,2AK, 2AKH, BK, BKH,2BK, 2BKH, 3BK
e) Adjustable sheaves: poly V-pulley, multi-pitch H, L, J, K and M
· Bore: pilot bore, finish bore, taper bore, bore for QD bushing
· Parts can be made according to drawings and/or samples
· we can offer the rang size diameter 62MM~2000MM
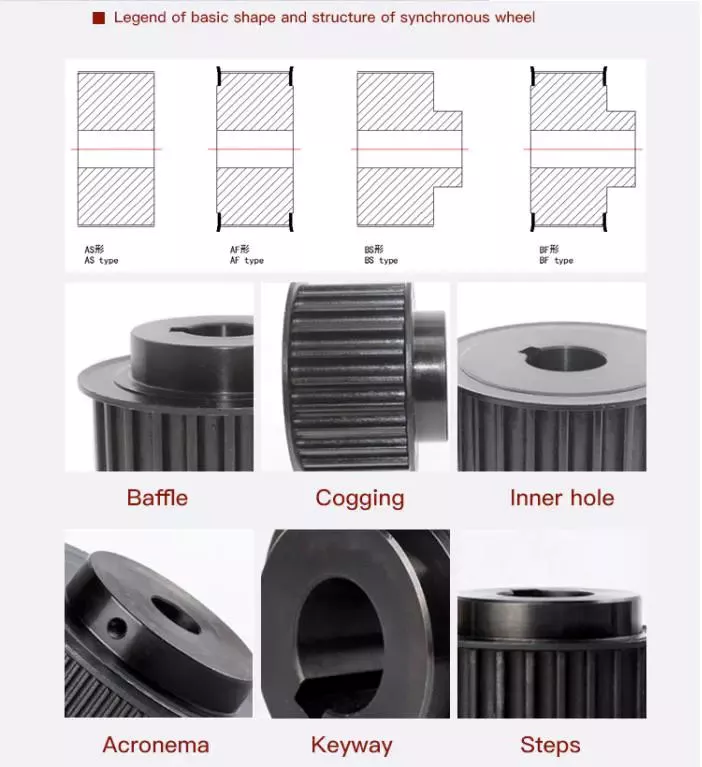
Prouducts show:
Our stock show
Our manufacture workshop
Packing show
Catalogue
FAQ
Q1. What is your terms of packing?
A: Generally, we pack our goods in single color box. If you have special request about packing, pls negotiate with us in advance, we can pack the goods as your request.
Q2. What is your terms of payment?
A: T/T 30% as deposit, and 70% before delivery. We’ll show you the photos of the products and packages
before you pay the balance. Other payments terms, pls negotiate with us in advance, we can discuss.
Q3. What is your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF.
Q4. How about your delivery time?
A: Generally, it will take 25 to 30 days after receiving your advance payment. The specific delivery time depends
on the items and the quantity of your order.
Q5. Can you produce according to the samples?
A: Yes, we can produce by your samples or technical drawings. We can build the molds and fixtures.
Q6. What is your sample policy?
A: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock, but the customers have to pay the sample cost and
the courier cost.We welcome sample order.
Q7. Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery
Q8: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
1. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them,
no matter where they come from.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | Type C |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Surface Treatment: | Polishing |
| Application: | Chemical Industry, Grain Transport, Mining Transport, Power Plant |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How does the diameter of a pulley affect its mechanical advantage?
The diameter of a pulley plays a significant role in determining its mechanical advantage. Mechanical advantage refers to the ratio of the output force or load to the input force or effort applied to the pulley system. Here’s how the diameter of a pulley affects its mechanical advantage:
1. Larger Diameter: When the diameter of a pulley increases, the mechanical advantage also increases. A larger diameter means that the circumference of the pulley is greater, allowing a longer length of rope or belt to be wrapped around it. As a result, a larger pulley requires less effort force to lift a given load. This is because the load is distributed over a greater length of rope or belt, reducing the force required to overcome the load.
2. Smaller Diameter: Conversely, when the diameter of a pulley decreases, the mechanical advantage decreases. A smaller diameter means that the circumference of the pulley is reduced, resulting in a shorter length of rope or belt wrapped around it. As a result, a smaller pulley requires more effort force to lift a given load. This is because the load is concentrated over a shorter length of rope or belt, requiring a greater force to overcome the load.
It’s important to note that while a larger diameter pulley offers a greater mechanical advantage in terms of reducing the effort force required, it also results in a slower speed of the load being lifted. This is because the longer length of rope or belt requires more input distance to achieve a given output distance. On the other hand, a smaller diameter pulley offers a lower mechanical advantage but allows for a faster speed of the load being lifted.
The mechanical advantage of a pulley system can be calculated using the formula:
Mechanical Advantage = Load / Effort
Where “Load” refers to the weight or force being lifted and “Effort” refers to the force applied to the pulley system. By adjusting the diameter of the pulley, the mechanical advantage can be optimized to suit the specific requirements of the application, balancing the effort force and speed of the load being lifted.

What is the importance of proper pulley alignment and tensioning?
Proper pulley alignment and tensioning are critical factors in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of pulley systems. They play a significant role in maximizing power transmission, minimizing wear and tear, and maintaining the overall performance and longevity of the system. Here’s the importance of proper pulley alignment and tensioning:
1. Power Transmission Efficiency:
Proper pulley alignment and tensioning ensure optimal power transmission efficiency. When pulleys are misaligned or belts/chains are improperly tensioned, energy is wasted due to increased friction and slippage. This results in decreased power transfer and reduced system efficiency. By aligning the pulleys parallel to each other and applying the correct tension to the belts or chains, the system can achieve maximum power transmission, minimizing energy losses.
2. Belt/Chain Longevity:
Correct pulley alignment and tensioning contribute to the longevity of belts and chains. Misalignment and inadequate tension can cause uneven wear, excessive stretching, and premature failure of the belts or chains. Proper alignment and tension distribute the load evenly across the belts or chains, reducing stress and extending their lifespan. This helps to avoid unplanned downtime, maintenance costs, and the need for frequent belt/chain replacements.
3. Reduced Noise and Vibration:
Improper pulley alignment and tensioning can lead to increased noise and vibration in the system. Misaligned pulleys or loose belts/chains can cause excessive vibration, resulting in noise, equipment damage, and discomfort to operators or nearby personnel. Proper alignment and tensioning help minimize vibration, ensuring quieter operation and a more comfortable working environment.
4. System Reliability and Safety:
Proper alignment and tensioning contribute to the overall reliability and safety of pulley systems. Misaligned pulleys or loose belts/chains can lead to unexpected failures, breakdowns, or accidents. Over-tensioning can also cause excessive stress on components and increase the risk of system failures. By maintaining proper alignment and tension, the system operates within its design parameters, reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures and ensuring the safety of operators and equipment.
5. Improved Performance:
Correct pulley alignment and tensioning enhance the overall performance of the system. Properly tensioned belts or chains provide better grip and traction, allowing for smoother and more precise movement of the driven components. This results in improved speed control, reduced slippage, and enhanced accuracy in applications such as conveyor systems, machine tools, and automotive engines.
6. Maintenance and Cost Savings:
Proper pulley alignment and tensioning can lead to significant maintenance and cost savings. Well-aligned pulleys and correctly tensioned belts or chains experience less wear and require fewer adjustments. This reduces the frequency of maintenance tasks, such as belt/chain replacements, realignments, and re-tensioning. Additionally, by maximizing power transmission efficiency and minimizing wear, proper alignment and tensioning help reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs.
In conclusion, proper pulley alignment and tensioning are crucial for achieving optimal power transmission efficiency, prolonging the lifespan of belts or chains, reducing noise and vibration, ensuring system reliability and safety, improving performance, and realizing maintenance and cost savings. It is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines and perform regular inspections and adjustments to maintain proper alignment and tension in pulley systems.

Can you explain the basic principles of pulley mechanics?
Pulley mechanics are based on a few fundamental principles that govern the operation of pulley systems. Here’s an explanation of the basic principles:
1. Mechanical Advantage: The primary principle of pulley mechanics is mechanical advantage. A pulley system allows for the multiplication of force applied to the rope or belt. By distributing the force over multiple segments of the rope or belt, the load becomes easier to lift or move. The mechanical advantage gained depends on the number of pulleys used in the system. The more pulleys in the system, the greater the mechanical advantage.
2. Force Transmission: When a force is applied to one end of the rope or belt, it creates tension that causes the pulley to rotate. As the pulley turns, the force is transmitted to the load attached to the other end of the rope or belt. This force transmission allows for the movement and manipulation of objects in pulley systems.
3. Directional Change: One of the key principles of pulley mechanics is directional change. A pulley system enables the operator to change the direction of the applied force. By redirecting the force along a different path, a pulley system allows for force to be exerted from a more convenient or advantageous position. This directional change is particularly useful in situations where the force needs to be applied vertically, horizontally, or at an angle.
4. Conservation of Energy: Pulley mechanics also adhere to the principle of conservation of energy. The work done on the load by the applied force is equal to the work done against the load’s weight. Through the pulley system, the input force is transformed into an output force that moves or lifts the load. The energy input and output remain the same, but the pulley system allows for the distribution and transformation of forces to achieve the desired mechanical advantage.
5. Speed and Torque Conversion: Pulleys can also be used to convert speed and torque in mechanical systems. By varying the size of the pulleys or using pulleys of different diameters, the rotational speed and torque can be adjusted according to the requirements of the system. This speed and torque conversion allows for the optimization of power transmission and the matching of different rotational speeds between input and output components.
6. Multiple Pulley Systems: Pulleys can be combined in systems to achieve increased mechanical advantage or to create complex motion patterns. In systems with multiple pulleys, such as block and tackle arrangements, the load is distributed over several segments of rope or belt, further reducing the effort required to lift heavy objects. These systems are often used in cranes, elevators, and other applications where heavy lifting is necessary.
These basic principles of pulley mechanics form the foundation for the understanding and application of pulleys in mechanical systems. By harnessing mechanical advantage, force transmission, directional change, conservation of energy, and speed/torque conversion, pulley systems provide a versatile means of lifting, moving, and manipulating loads in various applications.


editor by CX
2024-03-29