Product Description
Ratchet Lever Pulley Lifting 3meters Construction Work and Moving
Vt leverblock features as belows:
1. capacity from 250kg to 9ton .
2. lifting height 1.5meters or as customers’ request .
3. hoist covers are made of high strength alloy steel , and impact-resistance, well safety the inside parts .
4. upper and lower hooks are made of high strength casted alloy steel and heat treated , which prevent the hooks breaking even when overloading , with safety latch .
5. Load chain : CHINAMFG high strength alloy steel .
6. overload safetyion is optional .
Specifications of VT lever block as belows:
| Modle | VL0.75 | VL1.5 | VL3 | VL6 | VL9 | |
| Capacity TONS | 0.75 | 1.5 | 3 | 6 | 9 | |
| Standard lift M | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Running test load KN | 11 | 22 | 44 | 73.5 | 110 | |
| Headroom(drawn close up) Hmin MM | 315 | 365 | 490 | 620 | 800 | |
| Effort required to lift max. load N | 134 | 196 | 324 | 343 | 357 | |
| No. of falls of load chain | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Load chain MM | 6×18 | 8×24 | 10×30 | 10×30 | 10×30 | |
| Length of lever handle MM | 288 | 418 | 418 | 418 | 418 | |
| Dimensions(mm) | A | 147 | 178 | 203 | 203 | 203 |
| B | 87 | 105 | 110 | 110 | 110 | |
| C | 126 | 146 | 193 | 235 | 337 | |
| E | 26 | 31 | 40 | 45 | 57 | |
| Net weight KG | 7 | 11 | 20 | 30 | 54 | |
Vt lever block pics:
VT lever hoist detailed pics as belows:
HangZhou CHINAMFG Hoisting Machinery plant has our own CHINAMFG chains factory and the chain size can be from 4mm-26mm. We asselble the chain hoist lever hoist. So for the price we have a big advantage.
For newest price please feel to contact us!
| Application: | Double Beam Crane, Gantry Crane, Bridge Crane, Tower Crane, Single Grinder Crane, Lifting Platform, Small Crane |
|---|---|
| Type: | Lever Hoist |
| Sling Type: | Chain |
| Lift Speed: | >8m/min |
| Maximum Lifting Height: | 20m |
| Chain Falls: | 2 |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do pulleys contribute to the operation of conveyor systems?
Pulleys play a critical role in the operation of conveyor systems by facilitating the movement of materials or products along the conveyor belt. Here’s how pulleys contribute to the functioning of conveyor systems:
1. Power Transmission: Conveyor systems typically utilize a motorized pulley, also known as a drive pulley or head pulley, which is connected to an electric motor. The motor rotates the drive pulley, which in turn moves the conveyor belt. The rotational power from the motor is transmitted to the belt through the drive pulley, enabling the continuous movement of the belt and the materials being conveyed.
2. Belt Tension and Tracking: Pulleys are used to maintain proper tension in the conveyor belt. Tension pulleys, also called idler pulleys, are strategically placed along the conveyor system to apply tension to the belt. These pulleys help to keep the belt taut and prevent slippage or sagging. Additionally, tracking pulleys are used to align the conveyor belt, ensuring it stays centered and runs smoothly along the intended path.
3. Load Support: Pulleys provide support for the conveyor belt and the load it carries. The belt wraps around the pulleys, and the load is distributed over the surface of the belt. Pulleys with larger diameters are often used at points where heavy loads are encountered to help distribute the load more effectively and prevent belt deformation or damage.
4. Directional Changes: Conveyor systems may require changes in direction to accommodate the layout or specific processing needs. Pulleys known as bend pulleys or snub pulleys are used to redirect the belt and change its course. These pulleys are designed to guide the belt smoothly around bends or corners without causing excessive stress or strain on the belt.
5. Speed Control: Pulleys can be utilized for speed control in conveyor systems. By using pulleys of different sizes or by employing variable speed drives, the rotational speed of the drive pulley can be adjusted, affecting the speed at which the conveyor belt moves. This allows for flexibility in the conveyance process, accommodating different material flow rates or specific operational requirements.
6. System Support and Stability: Pulleys, along with their associated support structures, provide stability to the conveyor system. They help to maintain the alignment and tension of the belt, preventing misalignment, vibrations, and excessive belt movement. Properly designed and maintained pulleys contribute to the overall reliability and smooth operation of the conveyor system.
Conveyor systems are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, mining, logistics, and warehousing. Pulleys are essential components that ensure the efficient and reliable movement of materials and products along the conveyor belt, enabling automated and continuous material handling processes.
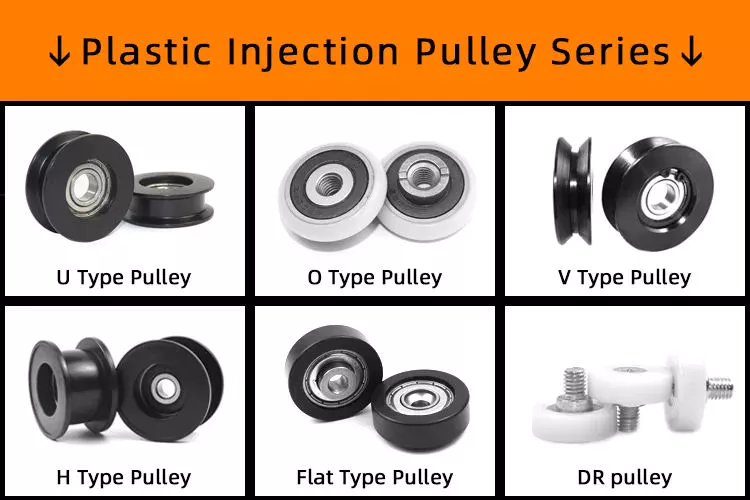
Can pulleys be used for both horizontal and vertical lifting?
Yes, pulleys can be used for both horizontal and vertical lifting. The versatility of pulley systems allows them to be utilized in various lifting applications, regardless of the direction of the load. Here’s how pulleys can be used for horizontal and vertical lifting:
1. Horizontal Lifting: In horizontal lifting scenarios, pulleys can be employed to change the direction of the force applied to the load. By using a combination of fixed and movable pulleys, the force can be redirected to pull the load horizontally. This is commonly seen in applications such as manual hoists or block and tackle systems used in construction, where heavy objects need to be moved horizontally across distances.
2. Vertical Lifting: Pulleys are widely used in vertical lifting applications, such as cranes, elevators, and lifting systems. In these setups, the pulleys are typically arranged in such a way that the load can be lifted vertically. By using multiple pulleys and ropes or cables, mechanical advantage can be achieved, making lifting heavier loads easier. The pulleys distribute the load’s weight across multiple lines, reducing the effort required to lift the load.
It’s worth noting that the number and arrangement of pulleys can vary depending on the specific lifting requirements. For example, a single fixed pulley can change the direction of the force but does not provide any mechanical advantage. On the other hand, systems with multiple pulleys, such as compound pulley systems or block and tackle setups, can provide significant mechanical advantage, making lifting heavier loads more manageable.
Whether it is horizontal or vertical lifting, the principles of pulley mechanics remain the same. Pulleys allow for force redirection, mechanical advantage, and load distribution, making lifting tasks more efficient and manageable. The specific configuration and setup of the pulley system will depend on the lifting requirements and the desired level of mechanical advantage.

How do pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting?
Pulleys play a crucial role in load distribution and lifting by providing mechanical advantage and distributing the load over multiple segments of rope or belt. Here’s how pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting:
1. Mechanical Advantage: Pulleys provide mechanical advantage, which allows for the multiplication of the force applied to the rope or belt. When a force is applied to one end of the rope or belt, it creates tension that causes the pulley to rotate. As the pulley turns, the force is transmitted to the load attached to the other end of the rope or belt. By distributing the load over multiple pulleys, the force required to lift the load is reduced, making it easier to lift heavier objects.
2. Load Sharing: Pulleys enable load sharing among multiple segments of the rope or belt. In systems with multiple pulleys, such as block and tackle arrangements, the load is distributed over several segments of rope or belt. Each segment carries a fraction of the load, reducing the strain on each individual segment. Load sharing ensures that the load is evenly distributed, minimizing the risk of overload or failure in any single segment.
3. Directional Change: Pulleys allow for directional change in the force applied to the load. By redirecting the force along a different path, pulleys enable lifting and moving loads in various directions, including vertically, horizontally, or at an angle. This directional change is particularly useful in situations where the force needs to be applied from a different position or angle than the original force application.
4. Balance and Stability: Pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting by providing balance and stability. The use of multiple pulleys in a system helps to distribute the load evenly, preventing excessive stress on any single point. This balanced distribution of the load enhances stability and reduces the risk of tipping or imbalance during lifting operations.
5. Control and Precision: Pulleys provide control and precision in load distribution and lifting. By adjusting the tension in the rope or belt, operators can achieve precise positioning and movement of the load. This level of control allows for accurate placement of heavy objects and ensures smooth and controlled lifting operations.
6. Increased Lifting Capacity: By leveraging mechanical advantage and load distribution, pulleys increase the lifting capacity. The mechanical advantage gained through the use of pulleys allows for the lifting of heavier loads with less effort. The load is distributed over multiple segments of rope or belt, reducing the force required to lift the load and enabling the lifting of objects that would otherwise be too heavy to lift manually.
Overall, pulleys contribute to load distribution and lifting by providing mechanical advantage, load sharing, directional change, balance and stability, control and precision, and increased lifting capacity. These contributions make pulleys an essential component in various lifting and load handling applications.


editor by CX
2023-12-01