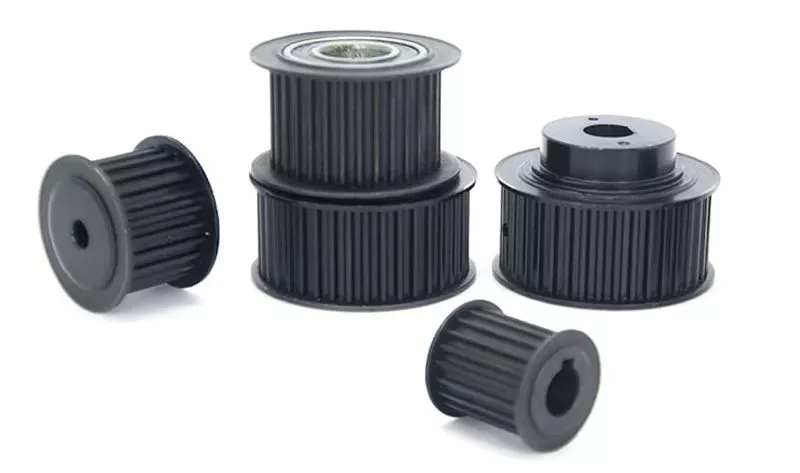
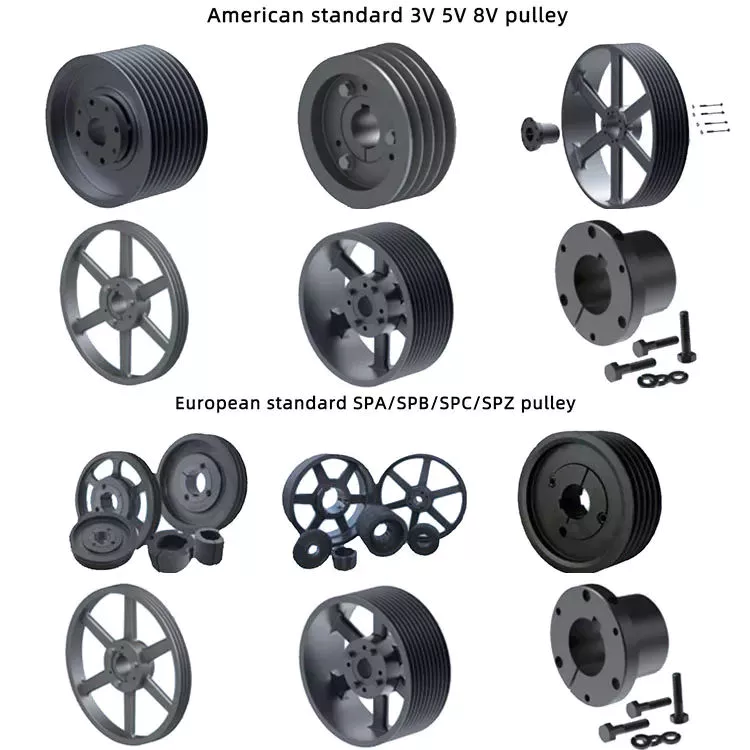
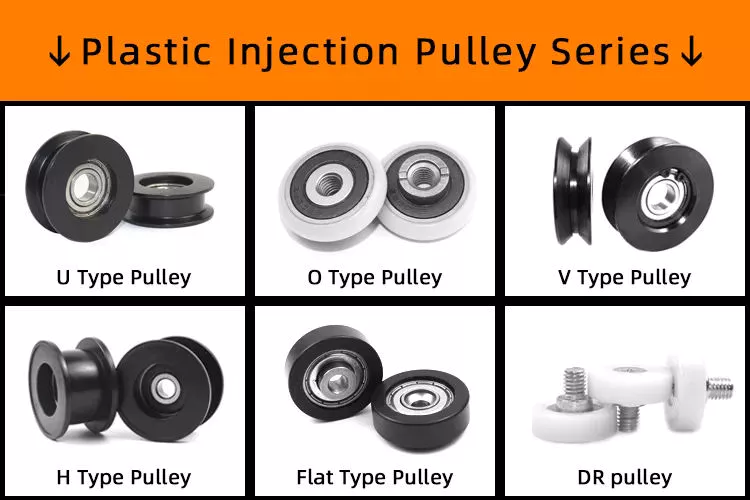
Product Description
Htd2m Htd3m Htd5m Htd8m Stainless Steel Timing Pulley
Synchronous belt pulley transmission is composed of an annular belt with equidistant teeth on the inner peripheral surface and a belt pulley with corresponding teeth. During operation, the belt teeth mesh with the tooth slots of the belt pulley to transmit motion and power. It is a new belt transmission that integrates the respective advantages of belt transmission, chain transmission and gear transmission.
Product Description
Main Features:
1. OEM/ODM tooth number from 14 to 72 timing pulley
2. Material can be designed by customer requirement
3. High torque series S2M S3M S5M S8M P2M P3M P5M P8M
4. Normal torque series MXL XL L H
5. High precision drive series 2GT 3GT 5GT 8YU
6. Light load drive series T5 T10
7. Heave load drive series AT5 AT10
8. Clamping Timing Pulleys S3M S5M S8M
| Product | standard timing belt pulley & idler pulley |
| Customized | OEM, drawings or samples customized |
| Teeth type | Normal Torque Drive Type:MXL,XL,L,H,XH,XXH High Torque Drive Type:S2M,S3M,S5M,S8M,HTD2M,HTD3M,HTD5M,HTD8M,P2M,P3M,P5M,P8M High Precision Position Drive Type:2GT,3GT,5GT,8YU Light Load Drive Type:T5,T10,T20 Heavy Load Drive Type:AT5,AT10,AT20 |
| Basic shape | Type A,Type B,Type D,Type E,Type F,Type K |
| Adaption | Adapt to 1/4 inch,5/16 inch,1/2 inch, 3/8inch, 2/25inch, 1/5inch belt |
| surface treatment | Natural color anodizing,Black anodizing,Hard anodizing,Ni-plating,Blackening |
| Material | 6061(aluminum),S45C(45# steel),SUS304(Stainless steel) |
| Bore | Pilot bore, Taper bore and Customized bore. |
| Tolerance Control | Outer diameter ±0.005mm Length dimension ±0.05mm |
| Standard | DIN, ISO/GB, AGMA, JIS |
| Teeth Accuracy | DIN Class 4, ISO/GB Classs 4, AGMA Class 13, JIS Class 0 |
| Weight | Max 15Tons |
| testing equipment | projecting apparatus,salt spray test,durometer,and coating thickness tester,2D projector |
| producing equipment | CNC machine,automatic lathe machine,stamping machine,CNC milling machine,rolling machine,lasering,tag grinding machine etc. |
| Machining Process | Gear Hobbing, Gear Milling, Gear Shaping, Gear Broaching,Gear Shaving, Gear Grinding and Gear Lapping |
| Application industry | Robot industry,Medical industry,Making machine industry,Automation industry,3C industry equipment,Packaging industry,UAV industry,New energy industry. |
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
| Main Markets? | North America, South America, Eastern Europe , West Europe , North Europe, South Europe, Asia |
| How to order? | * You send us drawing or sample |
| * We carry through project assessment | |
| * We give you our design for your confirmation | |
| * We make the sample and send it to you after you confirmed our design | |
| * You confirm the sample then place an order and pay us 30% deposit | |
| * We start producing | |
| * When the goods is done, you pay us the balance after you confirmed pictures or tracking numbers. | |
| * Trade is done, thank you!! |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Certification: | CE, ISO |
|---|---|
| Pulley Sizes: | Type A |
| Manufacturing Process: | Casting |
| Material: | Alloy |
| Surface Treatment: | Electroplating |
| Application: | Automation Equipment |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do multiple pulleys in a block and tackle system work together?
In a block and tackle system, multiple pulleys are used in combination to create a mechanical advantage, allowing for easier lifting of heavy loads. The pulleys in a block and tackle system work together in the following manner:
1. Load Distribution: The weight of the load to be lifted is distributed over multiple strands of rope or cable that pass through the pulleys. This distribution of weight helps in reducing the force required to lift the load.
2. Mechanical Advantage: The mechanical advantage in a block and tackle system is achieved by increasing the number of rope segments that support the load. Each additional pulley increases the number of rope segments, which in turn reduces the amount of force needed to lift the load. The mechanical advantage is equal to the number of segments of rope supporting the load.
3. Tension Distribution: As the load is lifted, the tension in the rope or cable changes. In a block and tackle system, the tension is distributed among the various segments of rope or cable connected to the pulleys. This distribution of tension ensures that the load is lifted evenly and prevents excessive stress on any single rope segment.
4. Rope Arrangement: The pulleys in a block and tackle system are arranged in two sets: the fixed pulleys and the movable pulleys. The fixed pulleys are attached to a fixed point, such as a beam or a ceiling, and do not move. The movable pulleys are attached to the load being lifted and can move freely. The arrangement of the pulleys determines the mechanical advantage and the direction of force required to lift the load.
By combining these principles, multiple pulleys in a block and tackle system allow for the effective lifting of heavy loads with reduced effort. The mechanical advantage provided by the pulleys makes it possible to lift loads that would otherwise be too heavy to lift manually. Block and tackle systems are commonly used in various applications, including construction, rigging, sailing, and theatrical setups.

How are pulleys used in manufacturing processes and assembly lines?
Pulleys play a crucial role in manufacturing processes and assembly lines, facilitating the movement of materials, components, and products. They are utilized in various ways to enhance efficiency, increase productivity, and streamline production. Here’s how pulleys are commonly used in manufacturing processes and assembly lines:
1. Conveyor Systems:
Pulleys are extensively employed in conveyor systems, which are integral to manufacturing and assembly lines. Conveyor belts or chains run over pulleys at different points along the line, transporting materials or products from one workstation to another. The pulleys help guide and support the conveyor belts or chains, ensuring smooth and controlled movement. By utilizing pulleys of different sizes or configurations, conveyor systems can be designed to accommodate various layouts, inclines, or speed requirements.
2. Material Handling:
Pulleys are used to facilitate the lifting, lowering, and movement of materials in manufacturing processes. Cranes, hoists, and lifting equipment often incorporate pulley systems to provide mechanical advantage and precise control over heavy loads. The pulleys, along with ropes, cables, or chains, allow operators to lift and position materials with minimal effort and improved safety.
3. Assembly Line Automation:
In automated manufacturing and assembly lines, pulleys are utilized in robotic systems to control the movement of robotic arms. The pulleys are incorporated into the mechanism that guides the cables or belts connected to the robotic arms. By adjusting the position and tension of the pulleys, precise and coordinated movements can be achieved, enabling efficient assembly processes.
4. Tensioning and Alignment:
Pulleys are crucial for maintaining proper tension and alignment in manufacturing processes. Tensioning pulleys are used to apply the appropriate tension to belts or chains, ensuring optimal power transmission and preventing slack or slipping. Alignment pulleys are employed to align belts or chains, minimizing wear, reducing vibrations, and prolonging the life of the components.
5. Power Transmission:
Pulleys are central to power transmission in manufacturing processes and assembly lines. They are used in conjunction with belts, chains, or gears to transfer rotational motion and power from one component to another. By selecting pulleys of different sizes or ratios, the speed and torque can be adjusted to suit specific production requirements.
6. Tool and Machine Positioning:
In manufacturing processes, pulleys are often integrated into tool positioning systems or adjustable machine setups. By using pulleys and cables, tools or machine components can be easily repositioned, allowing for quick changeovers or adjustments to accommodate different workpieces or production tasks.
Overall, pulleys are indispensable in manufacturing processes and assembly lines, enabling efficient material handling, precise movement control, proper tensioning and alignment, power transmission, and flexible tool positioning. Their use contributes to increased productivity, improved workflow, and enhanced automation in the manufacturing industry.

In which industries are pulleys extensively used?
Pulleys are extensively used in various industries for a wide range of applications. Here are some of the industries where pulleys find extensive use:
1. Manufacturing and Industrial: Pulleys are widely used in manufacturing and industrial settings. They are employed in conveyor systems for material handling, assembly lines, and production processes. Pulleys are also utilized in machinery and equipment such as pumps, compressors, generators, and conveyors. These industries rely on pulley systems for efficient movement of materials, power transmission, and mechanical advantage.
2. Construction and Engineering: The construction and engineering industries heavily rely on pulleys for lifting and moving heavy loads. Cranes, hoists, and winches utilize pulley systems to provide mechanical advantage and precise control over lifting operations. Pulleys are also employed in scaffolding systems, elevators, and material handling equipment used in construction projects.
3. Mining and Quarrying: In mining and quarrying operations, pulleys are used in various applications. They are utilized in conveyor systems to transport bulk materials such as coal, ore, and aggregates. Pulleys play a crucial role in mining equipment such as crushers, screens, and excavators, enabling efficient material handling and processing.
4. Transportation and Logistics: The transportation and logistics industries utilize pulleys in various ways. Pulleys are integral components in vehicles, including cars, trucks, buses, and trains. They are used in engines, power steering systems, alternators, and air conditioning systems. In logistics, pulleys are employed in conveyor belts and sorting systems for efficient movement of packages and goods in warehouses and distribution centers.
5. Agriculture and Farming: Pulleys have significant applications in the agriculture and farming sectors. They are used in machinery such as tractors, combines, and harvesters for power transmission and drive systems. Pulleys are also utilized in irrigation systems, grain elevators, and feed processing equipment.
6. Marine and Offshore: Pulleys find extensive use in marine and offshore industries. They are employed in shipbuilding, offshore drilling rigs, and maritime equipment. Pulleys are used in winches, cranes, anchor systems, and rigging applications. They enable safe and efficient lifting, lowering, and positioning of heavy equipment and cargo on ships and offshore platforms.
7. Energy and Utilities: The energy and utilities sectors utilize pulleys in power generation and transmission systems. Pulleys are used in turbines, generators, and power plants to transfer rotational motion and transmit power. They are also employed in renewable energy systems such as wind turbines and hydroelectric plants.
8. Entertainment and Stage Production: Pulleys have applications in the entertainment and stage production industries. They are used in theater rigging systems, concert stages, and amusement park rides. Pulleys enable the controlled movement of scenery, lighting equipment, and performers, ensuring smooth and precise operations.
These are just a few examples of the industries where pulleys are extensively used. Pulleys play a crucial role in a wide range of applications, providing mechanical advantage, power transmission, and efficient movement of loads in numerous industrial sectors.


editor by CX
2024-04-09